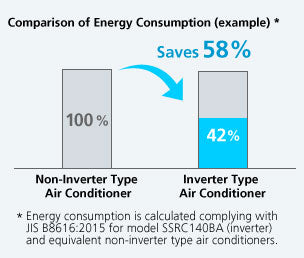
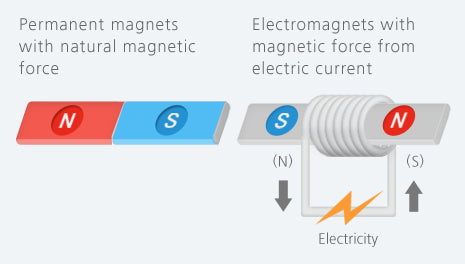
Perfecting the Air
Through Perfecting the Air, Daikin strives to make the world’s spaces happier and more comfortable.
Products
FAQ
Split System Heat Pumps
Cool and heat your home using renewable energy and hybrid solutions
Multisplit Heat Pumps
Heat or cool your entire home
Ducted Heat Pumps
Whole home heating & cooling system
Air Purifiers
Improve the indoor air quality of a specific room or space
Altherma Hot Water Heating
Innovative hydronic heating & cooling system